Engineer Solutions to Real World Problems!
The Engineering and Engineering Technology Department is home to three undergraduate programs: two ABET-accredited professional engineering programs (engineering with three options and environmental engineering) and an engineering technology program. Explore below to learn more about our degree paths and accreditation.
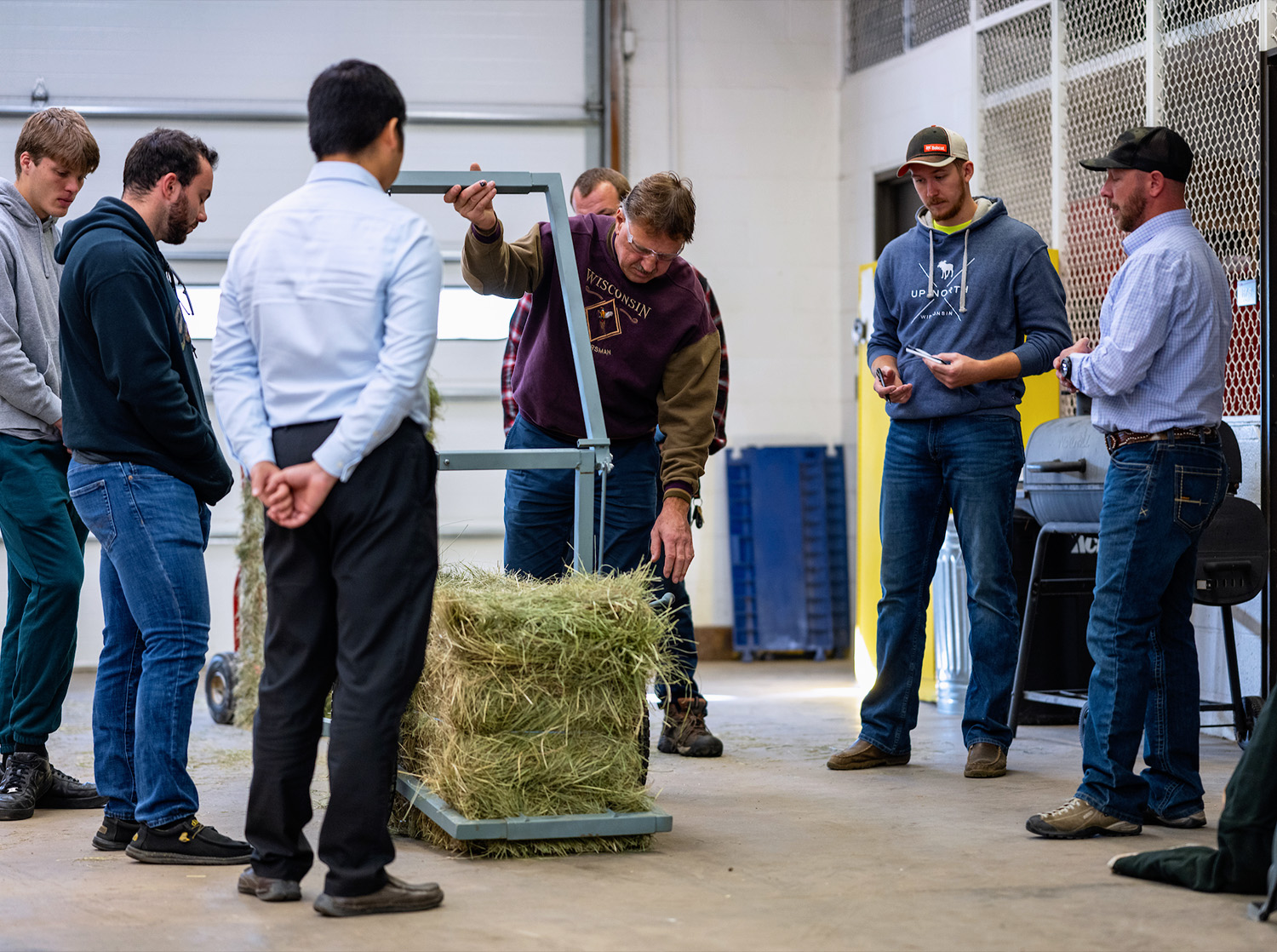

Engineering versus Engineering Technology?
What's the difference? Let's break it down!
- Professional engineering and engineering technology programs are separate but closely related.
- Professional engineering programs are more theoretical and focus on conceptual design, requiring higher level math and calculus-based physics.
- Engineering technology programs are more practically-focused and spend more time on applied problem-solving and engineering.
- Career paths of professional engineering and engineering technology graduates often intersect in related but different capacities. Many engineering applications have both professional engineers and engineering technologists working on the same project! For example, professional engineers may design a machine, waterway or food processing line, while engineering technologists would work with the engineers, skilled trades and technicians to inspect, test, validate and/or commission the new device.
Environmental Engineering (Major)
Environmental engineers are passionate about our natural world and seek to create solutions for society’s complex environmental problems.
Engineering (Major)
As an engineering major, you'll have the choice to focus on one of three options: Machinery Systems, Food and Process Systems or Natural Resources and Environmental Systems.
Engineering Technology (Major and Minor)
Engineering technology majors select an option to focus on from one of four areas: Agricultural Systems Management (ASM), Civil and Environmental Engineering Technology (CEET), Food and Bioprocessing Technology (FBS) or Test Engineering Technology (TET).You can also choose to minor in engineering technology.
ABET Accreditation
Engineering
The engineering program is accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of The Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET), under the commission's General Criteria and Program Criteria for Agricultural and Similarly Named Engineering Programs. ABET is a non-governmental organization in the United States that is the global accreditor of college and university programs in applied science, computing, engineering and engineering technology. More information about ABET can be found at www.abet.org.

Program Educational Objectives and Student Outcomes
Three to five years after graduation, graduates of the engineering program will be independently applying their knowledge, skills and abilities to identify, analyze and provide solutions to agricultural and related engineering problems. Graduates will be effectively communicating their ideas with colleagues, peers, clients and other stakeholders. They will be effective leaders and team collaborators. Graduates of the program will maintain the integrity of the engineering profession, engage in lifelong learning and recognize the value of engaging in a global society through self-study, continuing education or graduate school.
Outcomes expected of students in the engineering program include the following abilities to:
- Identify, formulate and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science and mathematics.
- Apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental and economic factors.
- Communicate effectively with a range of audiences.
- Recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental and societal contexts.
- Function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks and meet objectives.
- Develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions.
- Acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
Environmental Engineering
The environmental engineering program is accredited by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of The Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET), under the commission's General Criteria and Program Criteria for Environmental Engineering and Similarly Named Engineering Programs. ABET is a non-governmental organization in the United States that is the global accreditor of college and university programs in applied science, computing, engineering and engineering technology. More information about ABET can be found at www.abet.org.

Program Educational Objectives and Student Outcomes
Three to five years after graduation, graduates of the environmental engineering program will be independently applying their knowledge, skills and abilities to identify, analyze and provide solutions to environmental and related engineering problems. Graduates will be effectively communicating with colleagues, peers, clients and other stakeholders. They will be effective leaders and team collaborators. Graduates of the program will maintain the integrity of the engineering profession, engage in lifelong learning, and recognize the value of engaging in a global society through self-study, continuing education or graduate school.
Outcomes expected of students in the environmental engineering program include the following abilities to:
- Identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying principles of engineering, science and mathematics.
- Apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs with consideration of public health, safety and welfare, as well as global, cultural, social, environmental and economic factors.
- Communicate effectively with a range of audiences.
- Recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental and societal contexts.
- Function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks and meet objectives.
- Develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret data and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions.
- Acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.